Published by: Diana Luai Awad, Dr Pharmacist on Wednesday 31.August.2022
Couvelaire Syndrome is a rare complication of pregnancy and is one of the most dangerous, life-threatening for both the mother and the child. It occurs in about 5% of all placental abruptions. Why does it develop, how does it manifest and what methods can save a woman and a baby?
What is a Couvelaire uterus?
Couvelaire syndrome, Couvelaire uterus, uteroplacental apoplexy – all these terms describe one condition in which bleeding occurs due to placental vessels’ damage. In the early stages, blood seeps into the decidua. Small hematomas are growing as bleeding continues, and form a retroplacental hematoma. It ultimately causes separation of the placenta1.
As bleeding progresses, the walls of the uterus may become infiltrated with blood. Occasionally, infiltrates reach under the serous membrane of the fallopian tubes, into the connective tissue of the broad ligaments, the ovaries, and also into the abdominal cavity. As a result of blood impregnation of the myometrium and damage to the neuromuscular apparatus, the uterus loses its ability to contract – this is how massive obstetric bleeding occurs. This is a very severe complication, which in 80% of cases occurs in the postpartum period2. It is responsible for 25% of the 358,000 maternal deaths each year2. Placental abruption is the most common condition responsible for massive obstetric bleeding.
Depending on the degree of separation of the placenta, there are three classes of abruption1:
- Class 1 – mild, in about 48% of cases, less than 25% of the area of the placenta exfoliates, the condition of the fetus remains practically unchanged
- Class 2 – moderate, in 27% of cases, exfoliates from 25 to 50% of the area of the placenta, fetal hypoxia occurs
- Class 3 – severe, 24% of cases, more than half of the placenta exfoliates, the fetus dies, there is a threat to the life of the mother.
Symptoms of Couvelaire syndrome
The main symptom of placental abruption is vaginal bleeding, which occurs in 80% of cases3. Bleeding can be significant enough to compromise the health of the mother and fetus for a short period. However, one must not forget that in 20% of women placental abruption leads to occult bleeding, which makes timely diagnosis difficult.
The development of Couvelaire syndrome can also be suspected in cases of1:
- pain in the abdomen or back, tenderness of the uterus – 70% of women;
- fetal distress – 66% of cases;
- hypertonicity of the uterus, high-frequency contractions – 35% of cases;
- preterm birth of unknown (idiopathic) etiology – 25% of cases.
With placental abruption, uteroplacental circulation quickly deteriorates, and fetal hypoxia occurs. It is manifested by abnormal heart sounds, increased heart rate. With the progression of hypoxia, it becomes rare, arrhythmic. In 15% of cases, the child dies3.
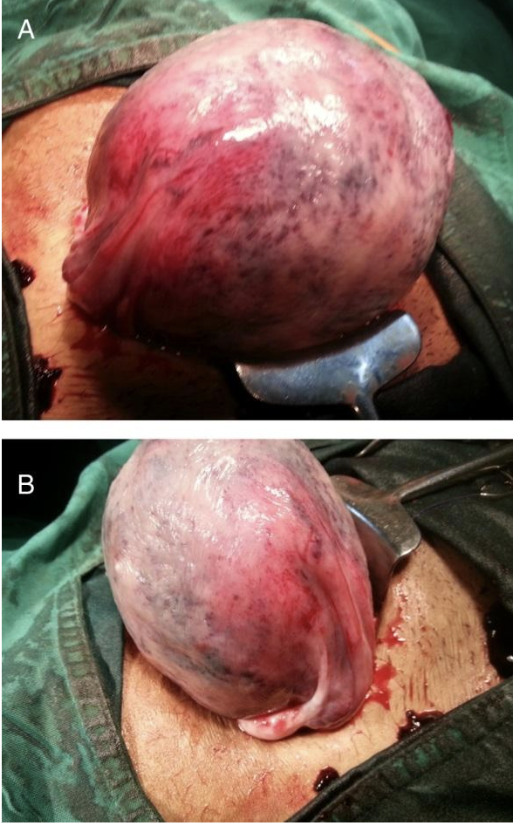
Source: Rathi M, Rathi SK, Purohit M, Pathak A. Couvelaire uterus. BMJ Case Rep. 2014 Mar 31;2014:bcr2014204211. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-204211. PMID: 24686812; PMCID: PMC3975566.
Causes of the Couvelaire uterus
The exact cause of Couvelaire uterus remains unknown, but scientists identified many risk factors that increase the likelihood of this formidable complication.
Among them3:
- injury to mother, eg motor vehicle collision, fall;
- unmarried or single mother;
- smoking;
- alcohol consumption;
- short umbilical cord;
- sudden uterine decompression, eg, premature rupture of membranes, first twin birth;
- retroplacental fibromyoma;
- history of placental abruption;
- chorioamnionitis;
- prolonged rupture of membranes — 24 hours or more;
- maternal age younger than 20 or older than 35;
- elevated levels of alpha-fetoprotein in the mother in the second trimester of pregnancy;
- subchorial hematoma.
A number of maternal diseases and conditions associated with an increased risk of detachment of a normally located placenta3: arterial hypertension, thrombophilia, gestational diabetes, diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2, hypothyroidism, anemia, uterine anomalies, history of caesarean section, history of miscarriage, preeclampsia.
How is the syndrome diagnosed?
Couvelaire uterus can only be confirmed visually, during surgery or biopsy. The doctor's task is to diagnose the abruption of a normally located placenta as soon as possible, based on the clinical picture and fetal data. Bloody discharge from the genital tract against the background of hypertonicity and asymmetry of the uterus, progressive fetal hypoxia are indications for immediate delivery by caesarean flow.
Treatment of Couvelaire syndrome
Caesarean section is necessary to stabilize the condition of both mother and child. It provides direct access to the uterus and its vessels, but the intervention may complicate the patient's coagulation status.
If after childbirth the uterus has contracted, but not enough, and bleeding, albeit not so pronounced, continues, urgent embolization of the uterine arteries with a gelatin sponge is indicated, which resolves within a month. This operation is performed by an endovascular surgeon in a specially equipped operating room.
In addition, hemostatic agents, uterotonics, in particular, oxytocin, ergometrine, prostaglandin F2 α, prostaglandin E1 analogues (misoprostol) are used.
- Oxytocin is considered the first line drug, causing relaxation of vascular smooth muscle, which can lead to hypotension and reflex tachycardia. It is given as a slow bolus followed by an infusion.
- Ergometrine is a second-line uterotonic drug that acts on the uterus and other smooth muscles. Causes severe nausea, vomiting, increased blood pressure, therefore contraindicated in eclampsia and other hypertensive conditions4.
If the uterus does not contract after the administration of uterotonics, the internal iliac arteries are ligated. In cases where even after this it is not possible to stop the bleeding, removal of the uterus may be required to save the patient's life. The operation is carried out in parallel with the replacement of blood loss, hemostatic therapy. Another non-surgical treatment option in cases where the patient does not respond to uterotonics is uterine balloon tamponade.
Bibliography
- Abruptio Placentae Clinical Presentation. URL: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/252810-clinical (available 23.08.2022).
- McLintock C., James A. H. Obstetric hemorrhage //Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis. 2011; 9 (8): 1441-1451.
- Tikkanen M. Placental abruption: epidemiology, risk factors and consequences //Acta obstetricia et gynecologica Scandinavica. 2011; 90 (2): 140-149.
- Trikha A., Singh P. M. Management of major obstetric haemorrhage //Indian journal of anaesthesia. 2018; 62 (9): 698–703.
Colleagues, haven't you joined our PharmaCourses of MENA region Telegram chats yet?
In the chats of more than 6,000 participants, you can always discuss breaking news and difficult situations in a pharmacy or clinic with your colleagues. Places in the chats are limited, hurry up to get there.
Telegram chat for pharmacists of MENA region: https://t.me/joinchat/V1F38sTkrGnz8qHe
Telegram chat fo physicians of MENA region: https://t.me/joinchat/v_RlWGJw7LBhNGY0